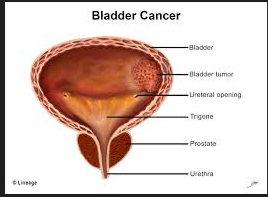
BLADDER CANCER
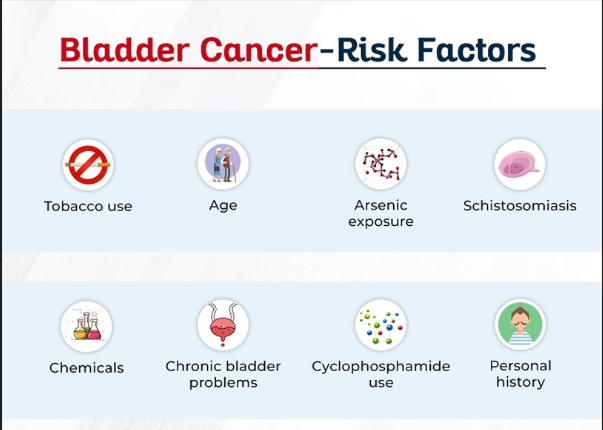
RISK FACTORS:
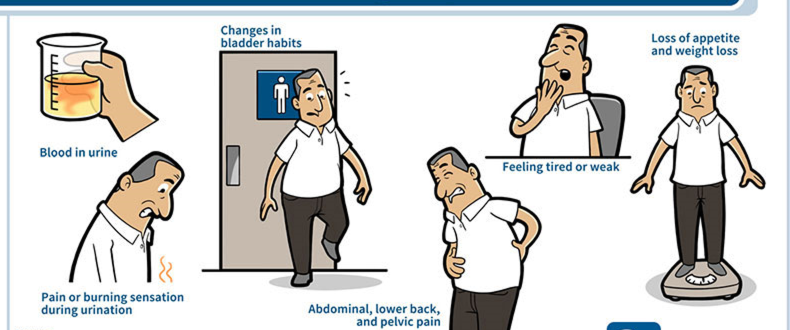
SYMPTOMS:
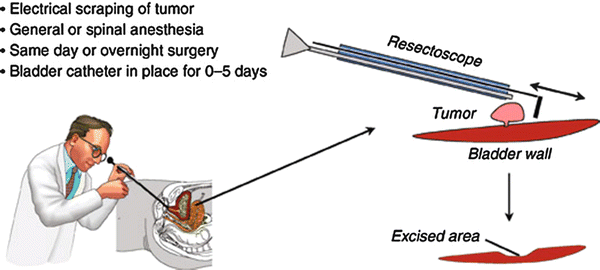
TREATMENT:
Treatment options depend on the type, stage, and grade of the tumor:
- Surgery:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): A minimally invasive procedure to remove the tumor through the urethra using a cystoscope without any cut in the body.
- Partial Cystectomy: Removal of part of the bladder, often used for localized cancer.
- Radical Cystectomy: Removal of the entire bladder, usually for invasive cancer. This may be followed by reconstruction or creation of a new way to store and pass urine
- Chemotherapy:
- Intravesical Chemotherapy: Directly administered into the bladder to kill cancer cells.
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Used for more advanced cancers, administered orally or intravenously.
- Radiation Therapy: Used primarily when surgery is not an option or to target specific areas of cancer spread.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells. Intravesical immunotherapy using Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is a common treatment for superficial bladder cancer.
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up is essential to monitor for recurrence and manage any long-term effects of treatment. This typically includes:
- Periodic Cystoscopy: To check for any new tumors or recurrence of cancer.
- Imaging Tests: To monitor for any spread or new growths.
For a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan, consult with a urologist


