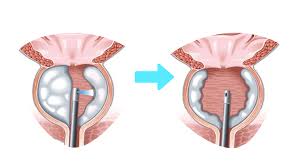
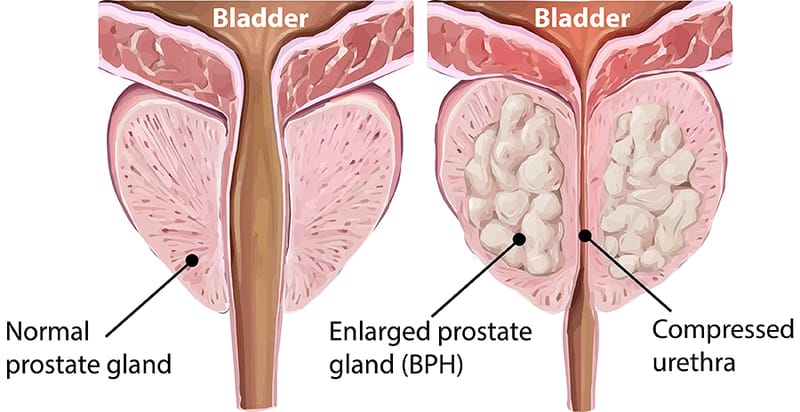
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT
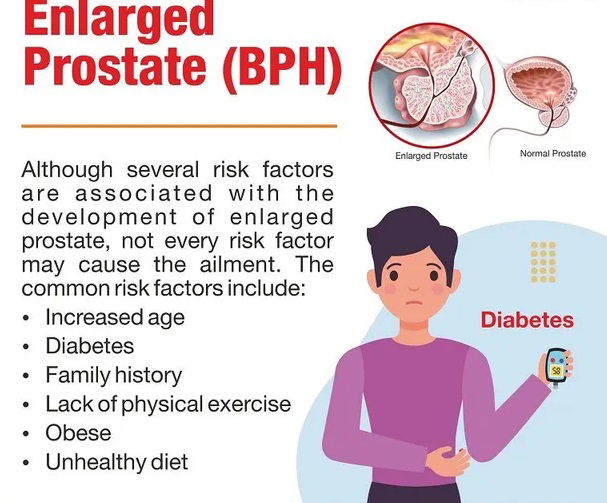
RISK FACTORS:
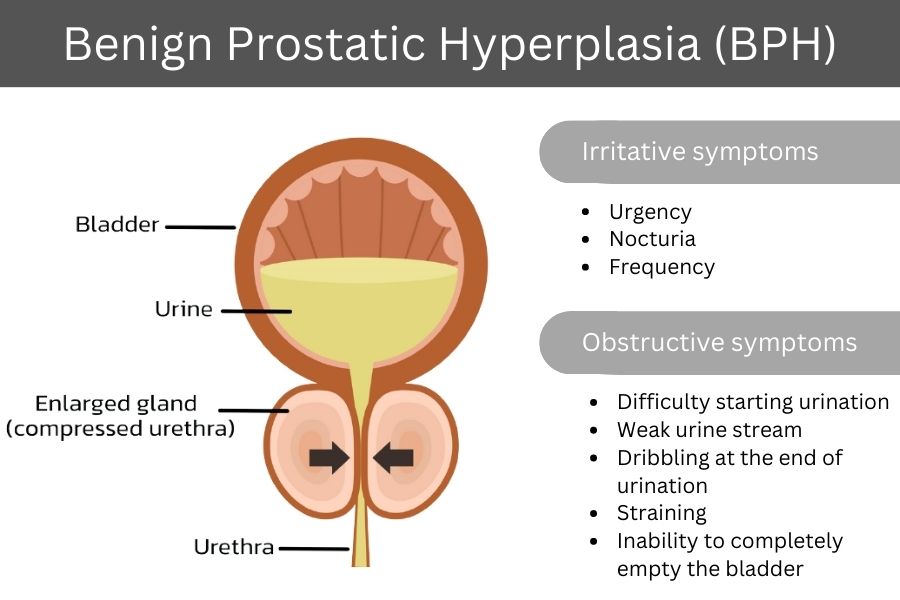
SYMPTOMS:
DIAGNOSIS:

TREATMENT:
Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms and their impact on quality of life. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Reducing fluid intake in the evening.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol, which can increase urinary urgency.
- Practicing double voiding (urinating, then trying again a few minutes later).
2. Medications:
- Alpha-Blockers: Relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck to improve urine flow (e.g., tamsulosin, alfuzosin).
- 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors: Shrink the prostate by blocking the hormone that causes prostate growth (e.g., finasteride, dutasteride). These may take several months to show results.
- Combination Therapy: Using both alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors for better symptom control.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
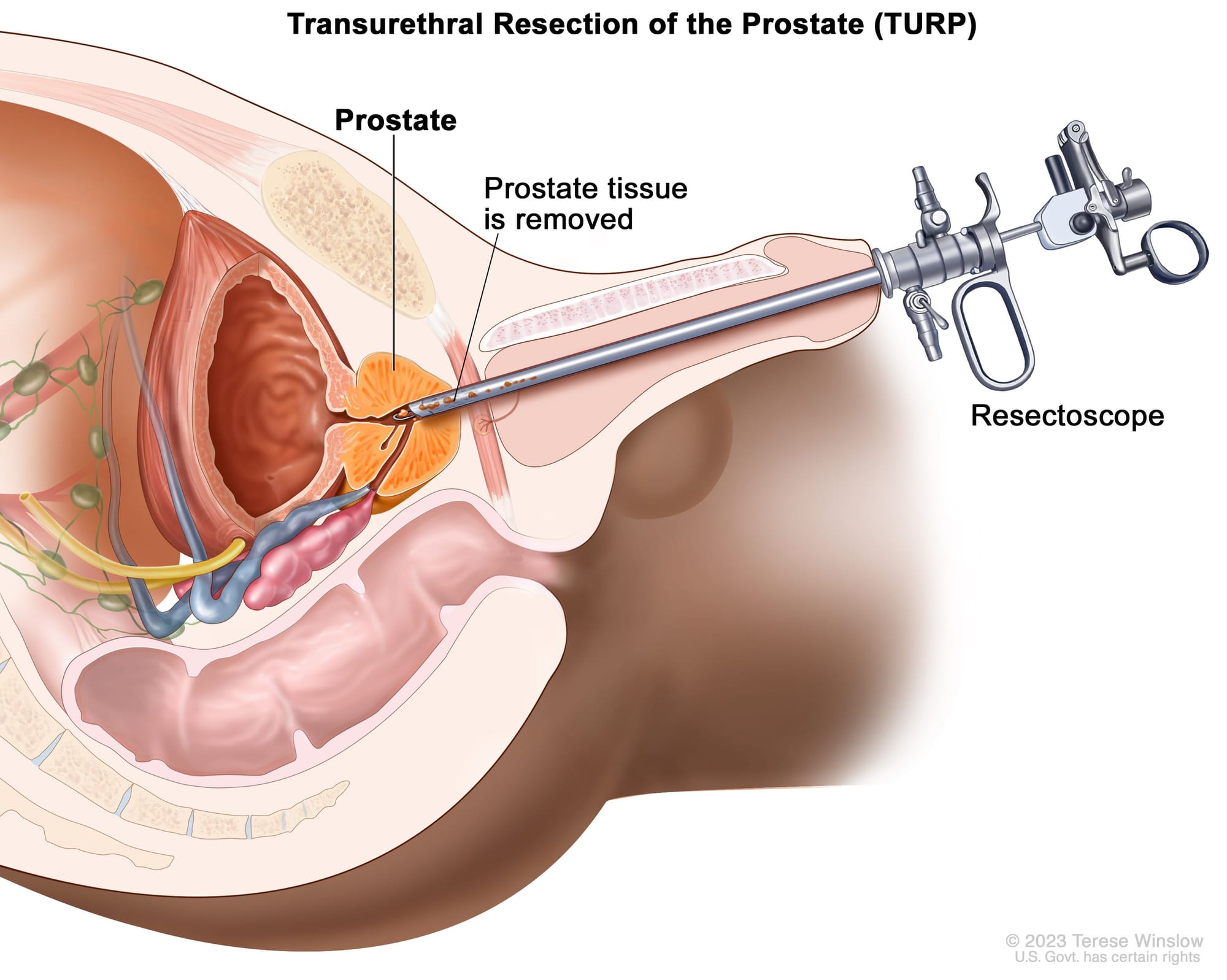
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): A surgical procedure where excess prostate tissue is removed using a scope inserted through the urethra.
- Laser Therapy: Uses laser energy to remove or destroy excess prostate tissue.
- Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA): Uses radiofrequency energy to destroy excess prostate tissue.
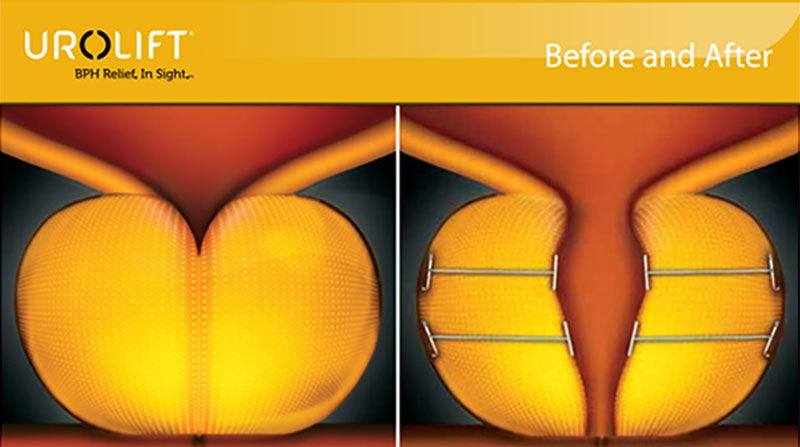
- Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL): Implants are used to lift and hold the enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra.
- Surgery:
- Open/Robotic simple Prostatectomy: Removal of the prostate through an incision in the abdomen. This is typically reserved for very large prostates or when other treatments are not effective.
COMPLICATIONS
If left untreated, BPH can lead to complications such as:
- Bladder Damage: Chronic obstruction can lead to bladder muscle damage or bladder dysfunction.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Due to incomplete bladder emptying.
- Kidney Damage: Severe bladder obstruction can lead to backflow of urine into the kidneys (hydronephrosis) and potential kidney damage.
- Bladder Stones: Formation of stones in the bladder due to incomplete bladder emptying.
If you experience significant changes in symptoms or have concerns about BPH, consulting with a urologist or healthcare provider is essential for appropriate evaluation and management.